Meta Tags For SEO: A Simple Guide For Beginners
Key Takeaways
- Meta tags in SEO play a crucial role by showcasing your webpage's value upfront, potentially boosting click-through rates.
- A Reddit blogger's experiment showed a 25% decrease in web traffic after removing title tags and meta descriptions but witnessed improvement after adding them back.
- Meta tags, including information like title, description, and keywords, help search engines understand and index your content, enhancing visibility in search engine results.
Editor’s Note: This post was originally published in February of 2024 and has been updated for accuracy and comprehensiveness.
Meta tags are one of the overlooked yet important parts of SEO. They show the value of your webpage upfront and can increase click-through-rates (CTR).
For instance, this blogger on Reddit ran an experiment on one of their websites that turns over $200,000 per year. They took off the title tags and meta descriptions. After two weeks, their web traffic went down by 25%.
They added the meta descriptions and title tags back, and the traffic improved:

What are Meta Tags?
Meta tags are HTML codes that provide information about a webpage to search engines and users.
They are added within the <head> section of an HTML document and include metadata such as the title, description, and keywords to summarize your page’s content to search engine crawlers.
This helps search engines understand the structure and content of your web page, which makes it easy to match your content with relevant user queries. All these can help improve your visibility in the search engine results pages (SERPs).
To view the Meta tag of any page, press Ctrl+U (you can try it on this page!).
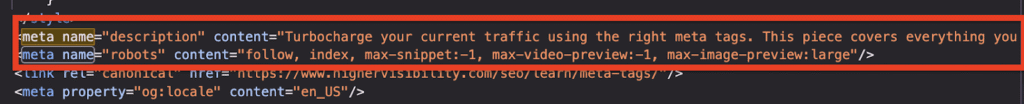
So why are these bunch of codes important for SEO? Let’s find out!
Why are Meta Tags Important for SEO?
Meta tags are important for SEO because they help search engine bots understand and index your webpage for the right search queries.
They provide a quick summary of your website content and help the bots understand what it’s all about, the keyword it’s relevant for, and how to rank it accordingly.
And since meta tags are codes in the headers, these bots can easily compare them to user queries and rank websites accordingly.
Meta tags can also influence click-through rate. Aside from AI Overviews or AI Mode answers, it’s the first thing users see after conducting a search query online.
Meta tags also:
- Impact how your page appears in search results.
- Encourage users to click on your link.
- Guide search engines on how to index your page.
- Contribute to a positive user experience and impact your site’s overall SEO performance.
Tip: Avoid using duplicate meta descriptions. They confuse search engine bots when they crawl and index your website.
10 Most Important Meta Tags You Need to Know for SEO
Many meta tags are used in SEO (some of which have become irrelevant as Google updates its algorithm). Here, we will focus on the ten most important meta tags you need to know for SEO.
1. Meta Description Tags
A meta description is a summary of your website page’s content. It helps search engines and readers understand what your page is about.
Like a movie trailer highlights interesting scenes to grab attention, a well-crafted meta description gives users a glimpse of “what’s in it for me” for readers.
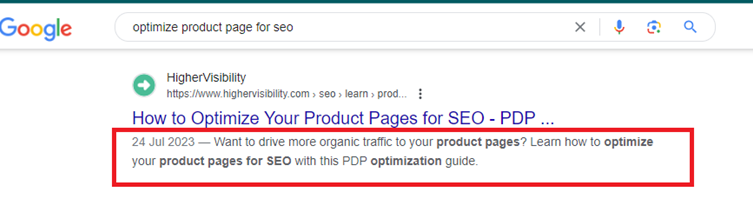
The meta description tag appears in a web page’s <head> section and is commonly (not always) shown in the SERP snippet alongside the title and page URL:
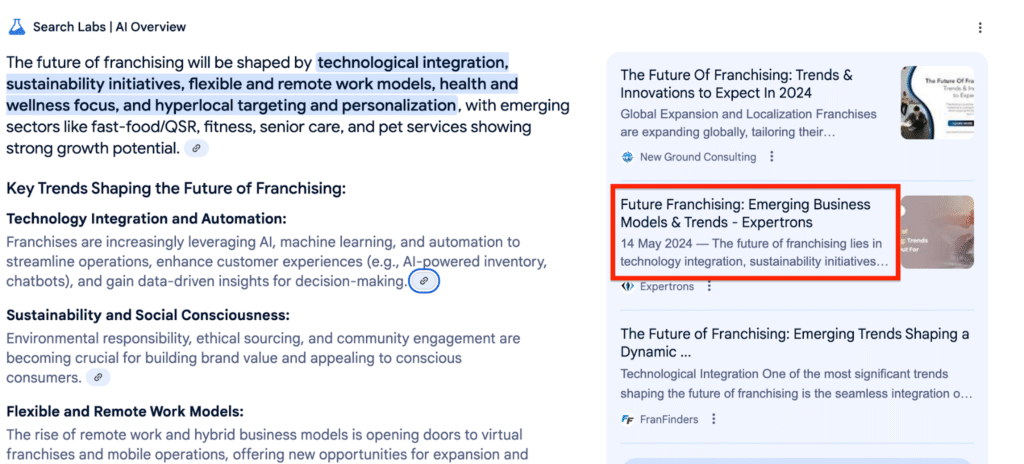
It’s also displayed on the AI Overviews source list:
According to a study, 62.9% of users click on a page because of the meta description. This shows that the right meta description can help you increase CTR. A higher CTR tells Google that your content is valuable and relevant, and the bots are more likely to push it up the search results for more visibility.
Best Practices:
- Limit meta descriptions to around 135 characters for brevity.
- Ensure it contains valuable information that matches users’ search intent. Google provides more context on this:

- Ensure that the description accurately reflects the content of the page.
- Let relevant keywords appear naturally for SEO.
- Create a unique meta description for each page to avoid duplication.
- Ensure the description is easy to read and understand.
2. Title Tags
Title tags are the clickable headlines you see on the search results pages. It explains what your page is all about and influences how search engine bots and users perceive it. This is how it looks in HTML code:

While traditional exact-match keywords are no longer a must-have to rank on the SERPs (including AIOs), you still need to make sure your titles are concise, eye-grabbing, and match user search queries. Most times, this requires turning your titles into statements that highlight the user’s end goal after reading (search intent).
For example, instead of “How to write better blog posts,” your title can be “How to write SEO blog posts that rank and convert in 2025.”
This title is relevant to the search query, contains the right keyword, and also conveys the value the content offers.
Why is this important?
Searchers are getting more precise with their queries. Instead of using short keywords, they type full questions or specific queries that reflect their intent to get specific results.
Katlyn Edwards, a contributor on Search Engine Land, adds that:
“Google’s AI systems will review your title to decide if your content is able to best answer the user’s query. Just the same as ranking in traditional search results, you’ll want a descriptive, keyword-focused title tag that summarizes your page’s content and reinforces your brand’s topical relevance and authority.”
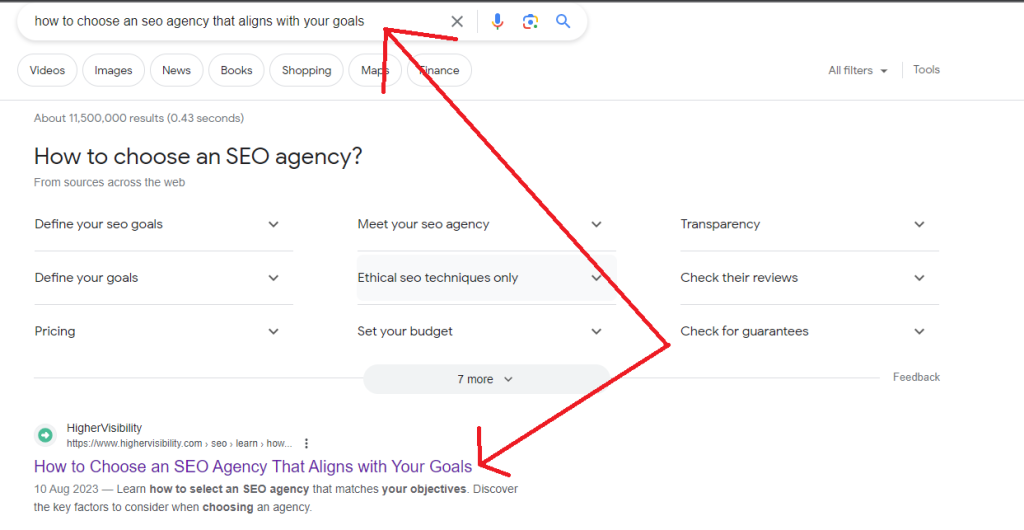
Here is a piece from our Co-Founder and Managing Partner at HigherVisibility, Adam Heitzman. It ranks first place on the search results for the keyword “how to choose an SEO agency that aligns with your goals” because the title tag is optimized correctly:
Best Practices
- Create unique titles for each page.
- Keep titles under 50-60 characters to avoid truncation in SERPs.
- Use A/B testing to test your headlines and see which one performs better in terms of clicks, impressions, and ranking.
- The target keyword should appear first and naturally in the title.
- Avoid clickbait titles (ensure titles accurately describe the page’s content).
- Add modifiers (‘How to,’ ‘Review,’ ‘Best,’ ‘Tips,’ ‘Top’) to your title tag.
- Make the title a descriptive, clear, and concise reflection of the page.
Here’s an extra tip from Katlyn Edwards:
“The best title tags will use a combination of these techniques, promising tangible results for the reader, but also piquing their interest. For example, a title like “15 Best Kitten Toys for Happy, Healthy Furry Friends (Vet-Approved)” combines emotional phrasing (“furry friends”), with functional phrasing (“happy, healthy” and “vet-approved”).”
3. Heading Tags (H1-H6)
Heading tags (H1-H6) help to structure content hierarchically on a webpage. They help users and search engine bots understand how to navigate your webpage, although differently. To search engines, they:
- Help the algorithm understand the organization, hierarchy, and relevance of your content.
- Show the relationship between different sections of your content.
- Help crawlers understand the topics and subtopics on the webpage.
- Allow Google to rank specific sections of your page based on how well they match a user’s search query.
To the readers, heading tags:
- Makes it easy for them to scan through your content and identify the section they’re most interested in.
- Provide a visual break in between blocks of text to improve readability.
- Create a logical workflow that guides them through the content step by step (especially if it’s a white paper or long-form blog post, like this one).
- Help them understand what each section is all about without the need to read everything word for word.
See this excellent illustration of a web page with heading tags and one without:

As you can see, when properly optimized with relevant heading tags and in the right order, they improve user experience and by default, your SEO performance.
Here are some tips on how to use heading tags across your article:
- Use H1 tags for the title of the web page.
- Use H2 and H3 tags for major subheadings.
- Use H4, H5, and H6 tags to provide further structure within H2s.
Just like this:
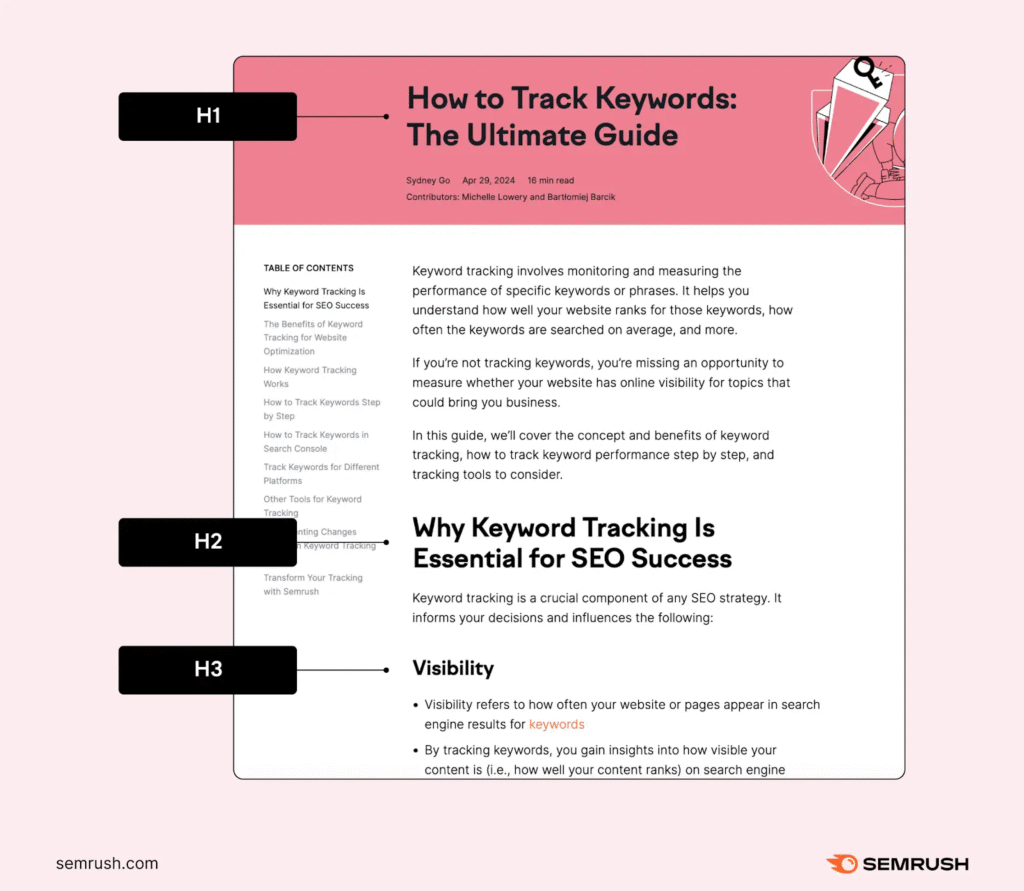
Best Practices
- Follow HTML structure guidelines for optimal SEO.
- Use only one H1 per page and it should not exceed 60 characters.
- Google recommends that you match your Title and H1 tag to increase ranking.
- Ensure your headings accurately reflect the sections they describe.
- Avoid excessive use for clarity.
- Distribute relevant keywords naturally among headers.
4. Robots Meta Tags
The meta robots tag instructs search engine crawlers on the amount of content they extract automatically from web pages for display on search results pages. It directs search engines on how to crawl and index web pages.
For example, robot tags offer directives like ‘noindex’ to prevent specific pages from appearing in search results and ‘nofollow’ to prevent crawlers from following certain links. While these tags don’t directly impact how high your page ranks, they control how search engines see your website.
Let’s assume you have pages with irrelevant content (which you need to add for some reason) or private information you don’t want to publicize. By using the ‘noindex’ attribute, search engine crawlers won’t show them on SERPs, keeping them from affecting your website’s SEO.
The meta tags are placed in the <head> section of your web page, like this:
| <!DOCTYPE html> <html><head> <meta name=”robots” content=”noindex”> (…) </head> <body>(…)</body> </html> |
Best Practices
- Use the ‘noindex’ attribute for pages with irrelevant, private, or unfinished content.
- Ensure the tags align with content strategy and site goals.
Pro Tip:
Sometimes, malicious crawlers ignore Robot meta tags. So, if you have web page information you don’t want to make public, use a more secure approach like password protection.
5. Viewport Meta Tag
With Google’s preference shift to mobile-first indexing, your website’s mobile responsiveness affects your SEO ranking. Yes, directly. This is where viewport meta tags become vital.
The viewport meta tag configures how a page scales and displays across various devices. It changes how the content is displayed and the layout of the webpage, too:
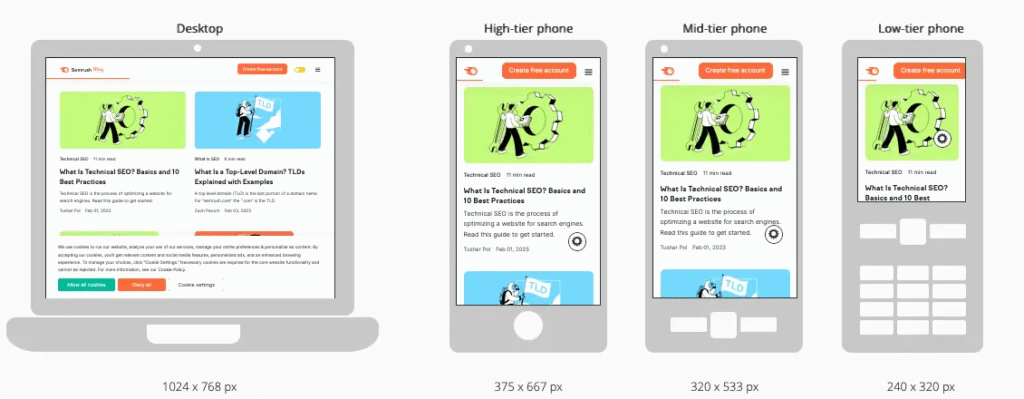
From the image above, you can see how the webpage is rendered across different devices. The desktop on the left shows the full-width layout, with content stretching across a wide screen as intended.
In contrast, the mobile devices on the right adapts to a smaller screen. The texts & images scale down to maintain readability and user friendliness.
Without the viewport meta tag, the browser will display the desktop version zoomed out, and users will have to pinch the page to read the content.
Nobody wants to do that.
This is how a mobile web page would look like with and without the viewport tag.
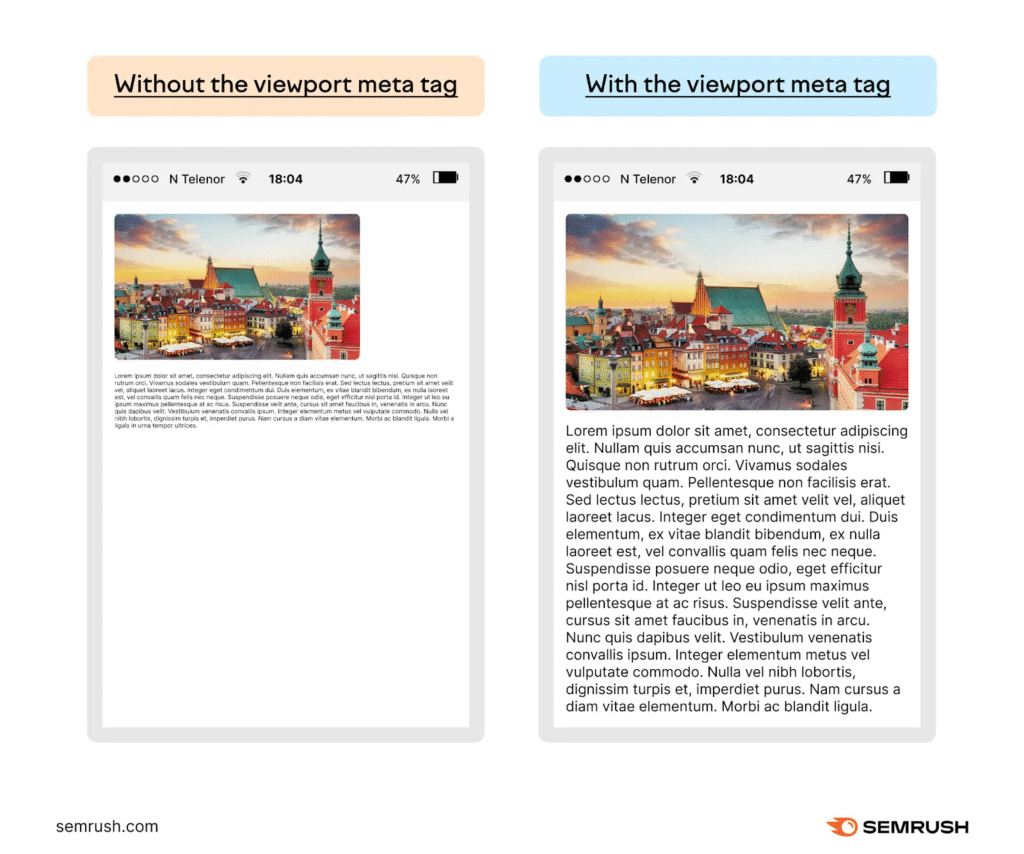
Because of the viewport tag, users are more likely to stay longer on your website. They don’t have to zoom in, scroll sideways, or struggle with poor formatting. All of these culminate in a better user experience and can likely increase time spent on page, which is a positive signal to search engines that your content is valuable and engaging.
Best Practices
- Set an initial scale for optimal viewing.
- Specify a width for responsive design.
- Test on various devices for compatibility.
- Prioritize user experience with smooth and adaptable layouts.
6. Social Media Meta Tags
When sharing your content link across social media platforms, it is vital to maintain a quality image and correct name, description, and URL. That’s what social media meta tags do. They let you control how your page content looks when shared on social media.
In 2010, Facebook introduced the Open Graph Protocol – a platform that allows you to create rich snippets for web pages. Social media platforms like LinkedIn and Twitter/X (Twitter tag cards) also embraced the trend. Here’s an example:

Here are the seven common OpenGraph tags:
- og:title: Put the desired title for display when your page is linked.
- og:url: Put your page’s URL.
- og:description: Create a concise page description; note that Facebook shows approximately 300 characters.
- og:locale: Specify your content’s language and region code (e.g., en_US).
- og:type: Describe the type of content (e.g., article, video).
- og:site_name: Add your website’s name.
- og:image: Specify the image URL you want displayed when your page is linked.
By optimizing these tags with relevant information, you can control the visual representation of your web page content on social media, increase click-through rates, and improve user experience.
7. Image Alt Attributes
Image alt attributes (also called alt text) are brief descriptions added to images in HTML. Here’s an example:

Ahrefs finds that 92.96% of global traffic comes from Google Search, Google Images, and Google Maps. This means having alt text on your web images can help you rank high in Google Image Search, Visual AI Overviews, and even traditional search results.
Aside from the visibility benefits, alt texts are also important for people who are visually impaired and use adaptive technology (think Braille devices, for example) to access web content. These technologies recognize and read the alt text aloud to help these categories of users understand the context of the images they can’t see.
Read more: How to make your website ADA-compliant.
Best Practices
- Optimize important images (like products or infographics) for Google Images search.
- Keep the alt texts short. The rule of thumb is to keep it under 125 characters.
- Add relevant keywords in your alt text to help search engines understand and rank the images accordingly.
Pro tip:
When writing alt text, ensure it describes your images very clearly, and add relevant keywords. This way, even if the pictures don’t load, users will still get the idea, and search engines can accurately index your content. Here’s an example:
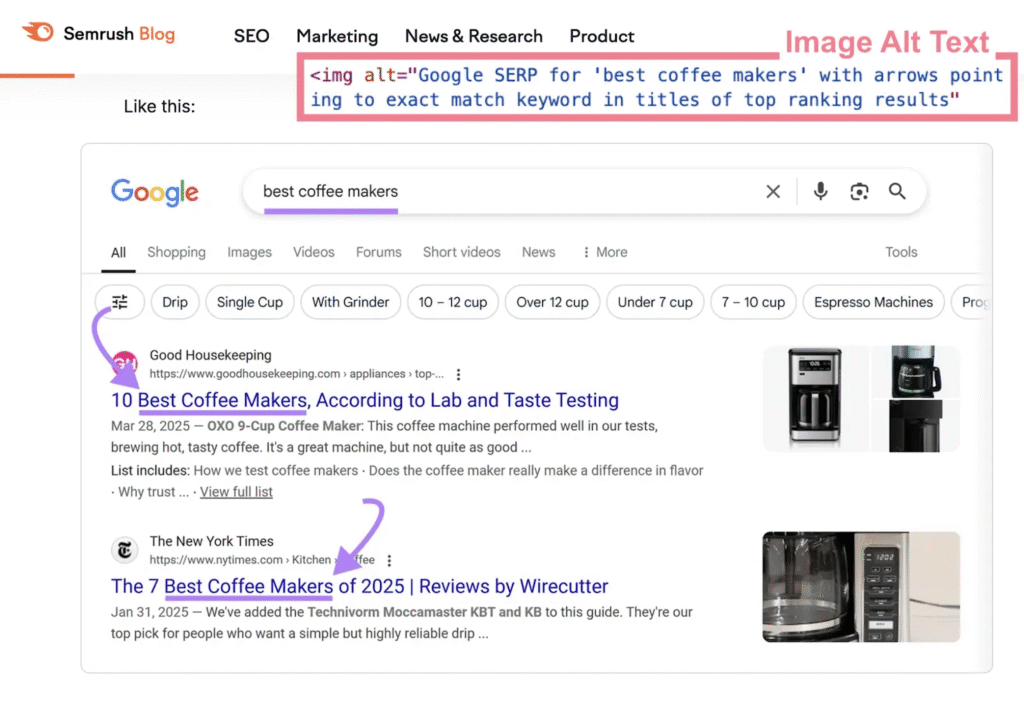
8. Nofollow Attributes
Adding external links to your content guides users and provides references to increase the credibility of your content.
However, while external linking provides value, too much of it can do the opposite. For instance, linking to low-quality or spammy websites can tank your rankings. This is why you should carefully vet the website you link to.
This is why you can always use the rel=“nofollow” attribute on links that you’re not entirely sure of. These tags tell search engine bots not to pass link equity to the receiving website, so if the page you linked to is down, it doesn’t affect your website.
Here are some links you should use the “nofollow” attributes for:
- Links to untrusted content.
- Paid or sponsored links.
- Links from comments or user-generated content that are prone to spam.
- Internal ‘Sign in’ links.
- Internal ‘Register’ links.
9. Schema Markup
Schema markup, known as structured data, is a code added to your webpage to help search engines understand its context and content.
By adding this code, you can “markup” specific details such as reviews, ratings, events, and product information on SERPs. This is displayed as “rich results” – a SERP (search engine result pages) feature that contains additional information about your web page, such as star ratings, reviews, FAQ, etc., depending on the schema implemented on the page.
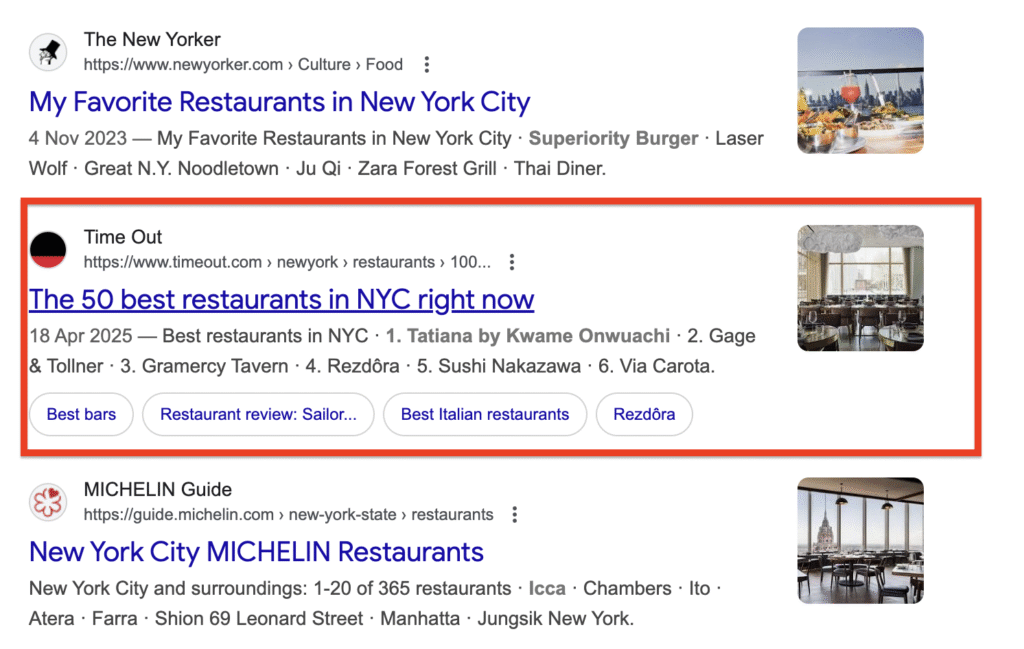
The best thing about schema markup is that it optimizes your website for conversational search queries.
Case in point: by adding the LocalBusiness schema on your Google business profile, you help search engines understand business details such as your name, address, phone number, and service area. This structured data increases your chances of appearing in local search results, map packs, and voice search queries like “what time does the nearest tailor open now?”
The same applies to other SERP features like AI Overviews, Featured Snippets, and People Also Ask boxes. These features are mostly triggered by conversational queries, and using the right markup in your content can help Google push your content to these high-visibility areas.
10. rel=“canonical” Link Tag
rel=“canonical” link tag helps specify which content is the main one and should be indexed when the same or similar content is available under different URLs.
Let’s assume you run an online store with similar product pages, but you want one page to carry the SEO weight. Adding a rel=“canonical” tag to that page tells search engines to focus there. This prevents duplicate content issues in search engine indexing.
Best Practices
- Align rel=“canonical” Link Tag with hreflang tags for international SEO.
- Don’t indicate different URLs as canonical for the same page.
Are Meta Keywords Important for SEO?
No, and here’s why:
Meta keywords were once important for SEO. Their primary purpose is to provide a list of keywords related to a web page’s content to help search engines understand what the page is about.
Now, search engines have evolved and their importance has diminished.
However, having meta tags helps with your user experience, which is why it’s still advisable today.
Common Meta Tag Mistakes to Avoid
Here are some common meta tag mistakes that can negatively impact your web page’s SEO:
- Duplicate Meta Tags: Using multiple meta tags with the same name can confuse search engines and may lead to penalties. Ensure each meta tag is unique to each page to avoid this issue.
- Missing or Incomplete Meta Tags: Failing to include important meta tags, such as the title tag or meta description, can make it difficult for search engines to understand your web page’s content and structure.
- Incorrectly Formatted Meta Tags: Using incorrect syntax or formatting can prevent search engines from reading your meta tags correctly. Always double-check your code for errors.
- Over-Optimization: Stuffing meta tags with too many keywords or using overly promotional language can be seen as spammy and may lead to penalties. Keep your meta tags natural and relevant.
How to Add Meta Tags to Your Website
Adding meta tags to your website can be done in several ways, depending on your platform and content management system (CMS). Here are some common methods:
- Manual Coding: If you’re comfortable with HTML, you can add meta tags manually by editing the HTML code of your web page. This method offers the most control but requires some technical know-how.
- CMS Plugins: Many CMS platforms, such as WordPress, offer plugins that can help you add and manage meta tags easily. Plugins like Yoast SEO or All in One SEO Pack are popular choices that simplify the process.
- SEO Tools: Some SEO tools, such as Ahrefs or SEMrush, offer features that can help you add and optimize meta tags. These tools often provide additional insights and recommendations to improve your meta tags.
Choose the method that best suits your needs and technical expertise to ensure your meta tags are correctly implemented.
How to Measure the Effectiveness of Your Meta Tags
Here are some common methods to evaluate their performance:
- Monitor your web page’s ranking in search engine results pages (SERPs) to determine the effectiveness of your meta tags. Ideally, higher rankings often indicate well-optimized meta tags.
- The CTR of your web page can provide insights into how compelling your title tag and meta description are. Higher CTRs suggest that users find your meta tags engaging and relevant.
- Tools like Google Analytics can offer detailed insights into how users interact with your web page. Track performance metrics such as bounce rate, average session duration, and user behavior to gauge the effectiveness of your meta tags.
- Conduct regular SEO audits to identify areas for improvement and determine the effectiveness of your meta tags. Tools like Screaming Frog or Sitebulb can automate this process and provide actionable recommendations.
Conclusion
Meta tags are the unsung heroes of SEO. While they may not carry much importance like content quality and keywords, they impact how you appear on the search results and user interaction with your content.
