Structured Data for SEO: Benefits to Visibility in 2025
Key Takeaways
- Schema markup was applied to improve search result listings for FreightFinder, leading to significant increases in organic traffic, ad revenue, and traffic value.
- Re-optimizing content, targeting branded and non-branded keywords, and running a PR campaign also contributed to enhanced brand visibility and domain authority.
- Schema markup played a crucial role in distinguishing offerings, providing structured data for search engines, and establishing a content knowledge graph for improved search ranking.
Are you struggling to capture attention in today’s evolving search landscape, where AI and Large Language Models (LLMs) are reshaping how content is found and cited? The key to unlocking greater visibility and relevance lies in providing search engines with structured, machine-readable data about your content.
Structured data, or schema markup, is the foundational layer that ensures your web pages are accurately understood by both traditional search algorithms and advanced AI models. It’s what transforms a good SEO strategy into a dominant one.
For a tangible example, consider, FreightFinder, a freight match company that faced a common challenge: improving search engine rankings and converting more visitors in a competitive market.
To help them achieve their goal, we:
- Applied schema markup to enrich their listings on the search results
- Re-optimized their content to highlight their unique offerings and boost their rankings for their core keywords.
- Optimized for branded and non-branded keywords to increase their appearance on search engines.
- Ran a PR campaign to increase their brand mentions online, and by extension, domain authority.
After the campaigns, they saw:
- 162% increase in organic traffic,
- 86% increase in organic ad revenue,
- 145% increase in organic traffic value.
While multiple strategies were at play, it was the schema markup that provided the critical foundation, enabling them to:
- Distinguish their offerings from the competition.
- Provide search engines with the structured data needed to rank their website for relevant search queries.
- Create a content knowledge graph for their brand online.
Schema markup is essential because it gives search engine bots enough information about your pages to understand precisely what they are about. The more context it has, the easier it is for users to find and engage with your products and services.
You can read the full case study on FreightFinder here.
If you’re looking to replicate this success and you’re yet to markup your web content, here are four (4) reasons why you should prioritize structured data.
Four Ways Structured Data Improves SEO Performance
Here are the top four benefits of using schema markup for SEO:
1. It helps AI search engines parse your content to rank it for relevant search queries
Unlike traditional search engines that scan meta descriptions or rely on keywords to understand what a web page is all about, LLMs (large language models) or AI search engines interpret and analyze content differently. They focus on semantic clarity, coherence, and logical order of your web content.
Here’s a breakdown of how these models parse your content:
Whenever a user conducts a search query (either on Google or LLMs), the algorithm doesn’t match the exact keywords to content that has the exact strings or close lexical variants. This would have been the usual process for traditional search engines.
Before LLMs process content, they first break it down into tokens. Each of these tokens is mapped into a numerical vector through an embedding layer to capture its semantic meaning (what the word means) and syntactic role (how it functions in a sentence).
In simple terms, this is how LLMs distinguish between queries like “comfortable shoes for running” and “running comfortably in shoes.”
This process is called embedding language models. It converts data (in this case, your content) into numerical representations and stores it in a vector database that LLMs can understand.
Like this:
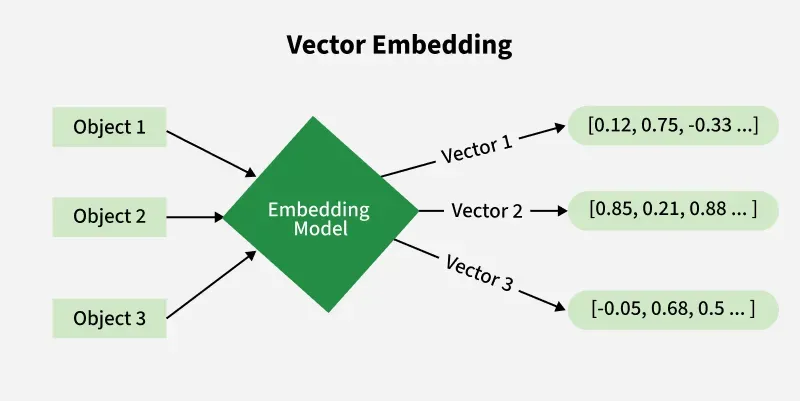
So, when a user enters a query, it is converted into numerical embeddings, which are semantically matched against the vector database. The system will then retrieve documents (or content) that are highly relevant to the user’s search and use the RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) framework to provide a context-rich response.
Here’s a visual representation of the RAG system:
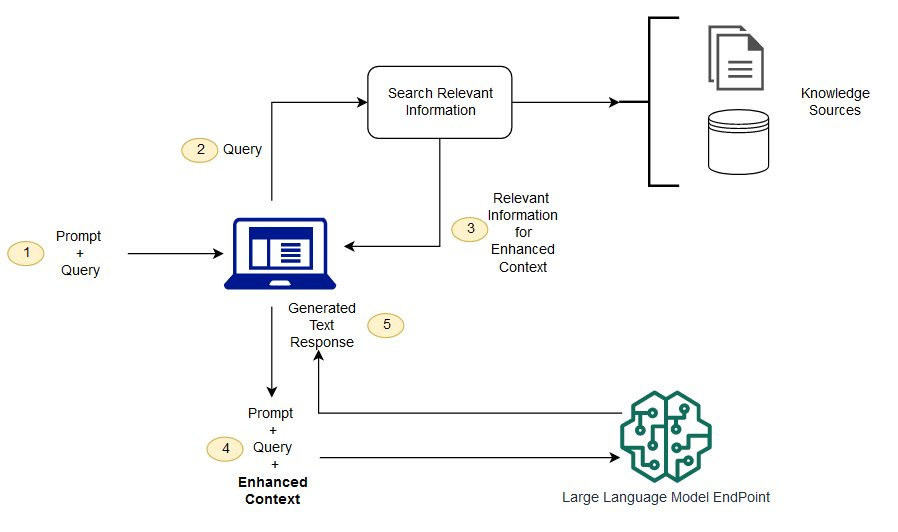
In simple terms, what matters for LLMs when they parse content is:
- How the content is structured.
- The hierarchy of information presented.
- Formatting cues like tables, bolded texts, and bullet points.
- Accurate and up-to-date.
This is where schema markup comes in.
Schema markup makes your web content machine-readable. It highlights the important aspects of your content and helps LLMs understand how it relates to user search queries. And because it appears as structured data, LLMs can quickly identify the key entities and relationships on your page without having to infer them from unstructured text.
In a sentence, structured data makes it easy for LLMs to understand:
- What your web page is all about,
- How it connects to related topics, and
- Which part of your content best answers a user search query.
For example, say a user types this query into Perplexity: “I’m looking for comfortable and stylish Nike shoes for women that are good for both casual wear and light workouts. Preferably something breathable, under $120, and available in neutral colors like white or beige. Can you show me the newest models or best-rated options? I’m located in Memphis, Tennessee.”
Here’s the output on Perplexity:
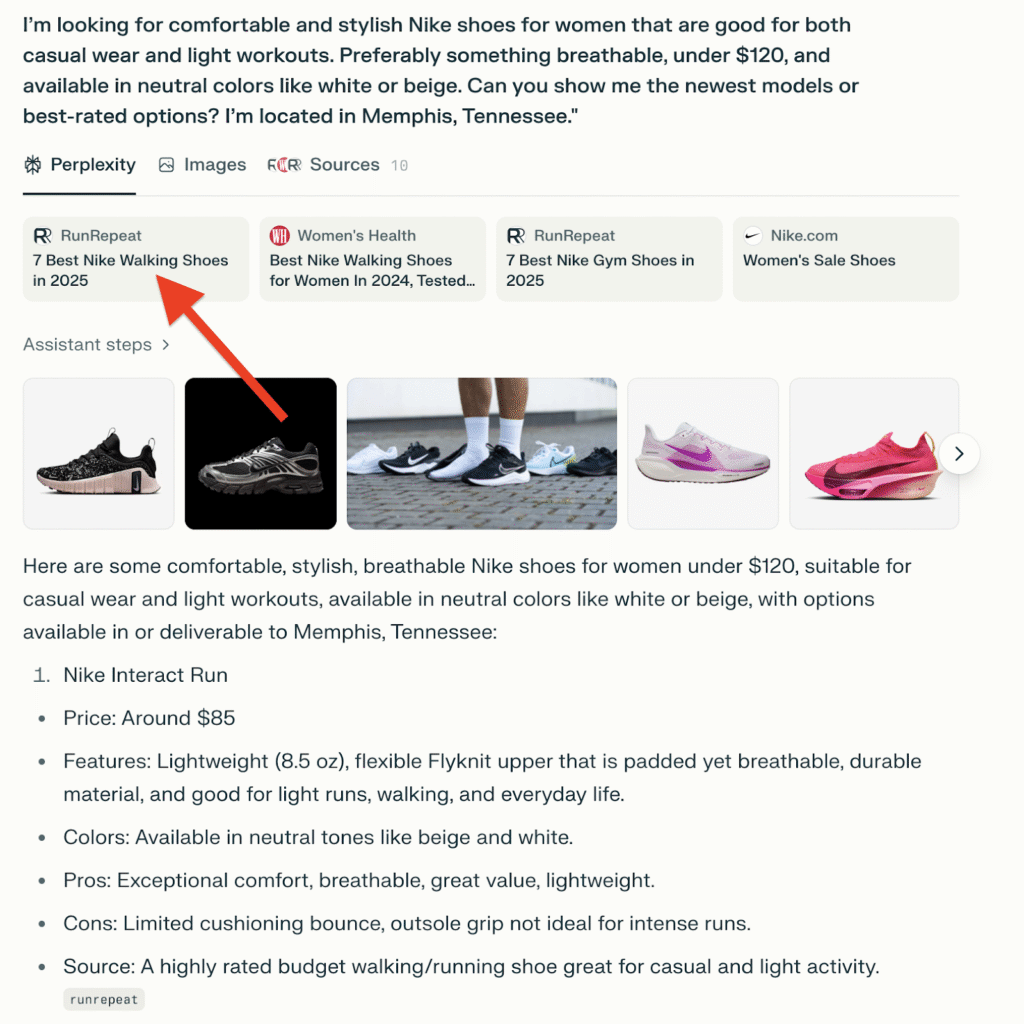
If your website has product page schema markup, the LLM can easily parse your content and extract key details, including the product name, brand (Nike), gender (women’s), category (shoes), price, availability, color options, and customer ratings.
For instance, the first blog cited is marked up with articles and breadcrumbs schema:
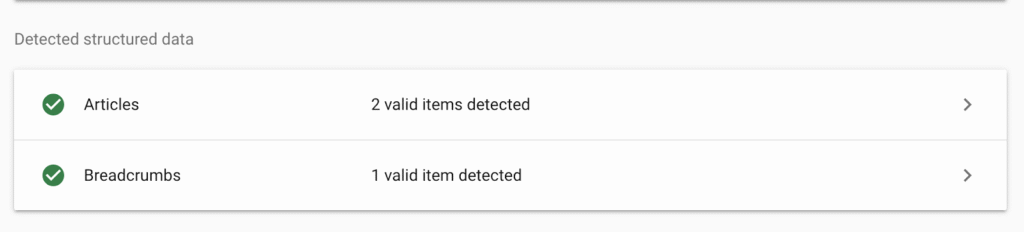
So, instead of guessing, LLMs can read this structured data directly to understand what your page offers. This increases your chances of appearing in AI responses.
2. It helps you achieve Google’s rich results, significantly boosting your CTR.
Rich results (or rich snippets) are enhanced search results displayed on Google search engine result pages. They highlight key details about a webpage in search results, such as reviews, images, page URLs, and even lists, to help searchers find information and make informed decisions fast.
The rich results stand out in search results and are more visually appealing than the standard search engine results pages.
This is how it looks:

The additional data displayed is extracted from the schema markup on a web page.
The advantage of rich results is that they help you take up more space in search results. You can showcase all the key information your searchers need, such as product ratings, prices, availability, FAQs, etc., to influence their decision on which brand offers the best value for their money. And compel them to click through.
Here’s an example from SoundGuys. It shows a brief overview of Beats Studio3, ratings, pros & cons – all the basic information the reader may be looking out for:
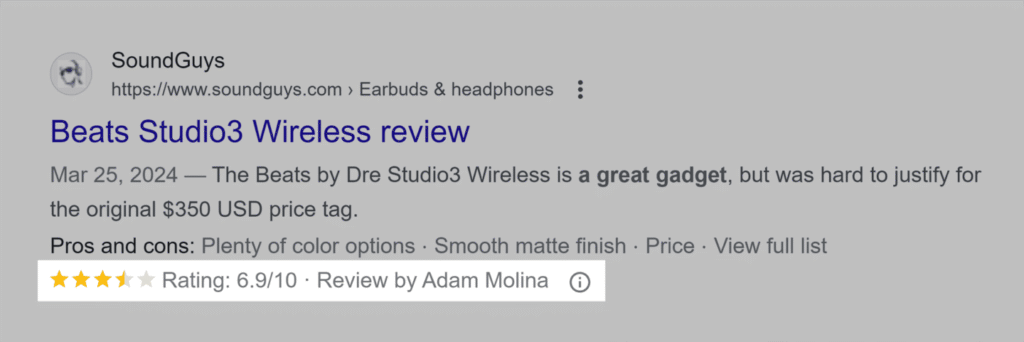
Research validates this, too. According to Google:
- Rotten Tomatoes added structured data to 100,000 unique pages and saw a 25% increase in click-through rate.
- Nesle measured pages with rich results and those without. The pages with rich results recorded an 82% increase in CTR compared to non-rich result pages.
That said, if there’s a decline in CTR, despite your high organic traffic and impressions, markup your content, especially your product pages. It can increase your visibility on AI search engines where users also make strategic decisions.
3. It helps you drive traffic outside traditional SEO
There are many ways users search today.
Previously, an online shopper might “google” the “best running shoes for women” before making a purchase.
The same shopper today might search on TikTok for reviews, use AI Overviews to get a summary of the top options, and ask ChatGPT for personalized recommendations, before they eventually visit a brand’s website or marketplace to make a final purchase.
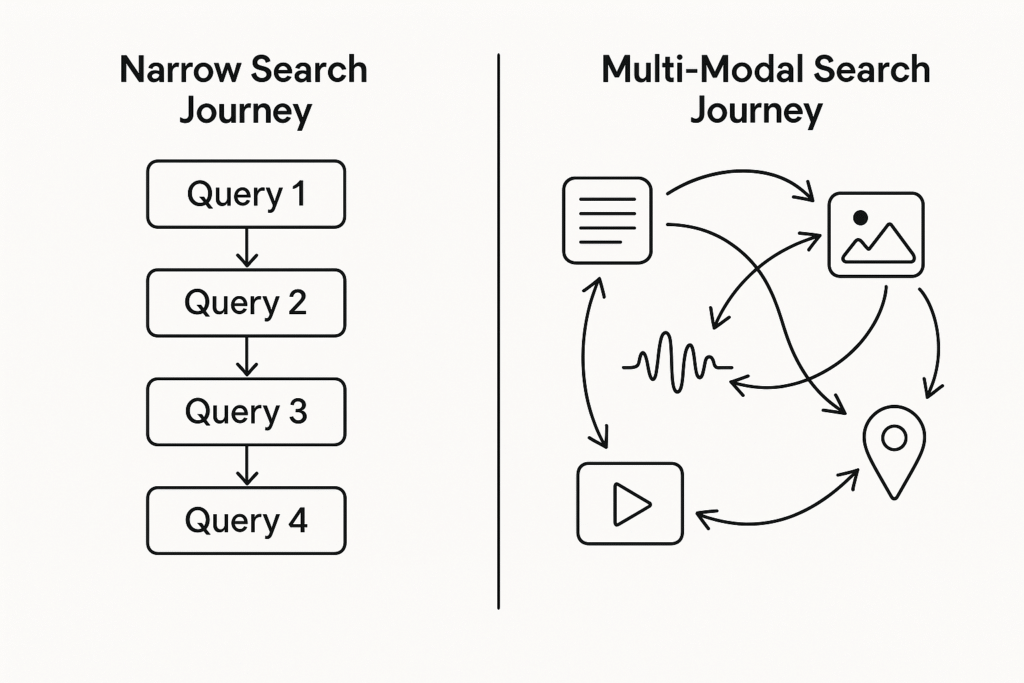
This is a multimodal search concept that explains the non-linear, multi-platform way users find information online. Instead of a single source, these searchers move fluidly between text, voice, image, video, and voice searches, and across multiple platforms at each step before making a choice.
Here’s a simple illustration of multi-modal search in action:
Let’s use voice search as a case study.
Voice searches have gone mainstream, thanks to the integration of voice assistants in mobile devices. As of 2025:
- Around 27% of people use voice search on their mobile devices.
- Siri has over 86.5 million users in the United States alone. That’s over 25% of the 340.1 million population.
- Near me and local searches dominate 76% of voice searches.
- 38.8 million people in the US use smart speakers for shopping-related activities.
[Source]
Since voice searches are often conversational and question-based, e.g. “Where is the best bakery near me? I need somewhere to get a (type of loaf– or any other specification)” or “Which dentist near me is open? I need to treat a germ issue,” schema markup optimization can help you rank better for these queries.
For example, with markups like FAQPage, HowTo, and LocalBusiness, these voice assistants can easily recognize the context of your content and extract specific answers to match user queries.
Simply put, schema makes your content easier for machines to find and serve direct answers to voice queries.
The same applies to image searches. Google launched Google Lens in 2017, and since then, the platform has generated over 20 billion searches per month. And 1 in every 4 of these searches has commercial intent.
Just like text, adding image schema markup helps search engines understand the content of your image and how it relates to the webpage.
For example, the ImageObject type and its related properties, such as caption, creditText, or AssociatedArticle, provide Google with detailed information about your website images.
Google specifically mentioned that using structured data on your webpage to display prominent baked-over image thumbnails, such as “Product,” “Recipe,” or “Video,” can increase your rankings for the rich results:

Google uses this data to match your images for relevant search queries, especially visual searches, which, by extension, drive targeted traffic to your website.
This multimodal parity also increases your digital footprint. You can rank across the multiple platforms your target audience uses during search.
Michael King, a colleague in the industry, explains how the multimodal approach helps you appear in LLM responses:
“Because routing decisions are modality-aware, having your information available in text, tables, images, videos, transcripts, and structured data gives you more entry points into the retrieval process. If the system decides a sub-query should be answered with a table and you only have prose, you’re invisible to that branch of the fan-out.”
4. It allows you to influence how search engines display your brand’s content to searchers
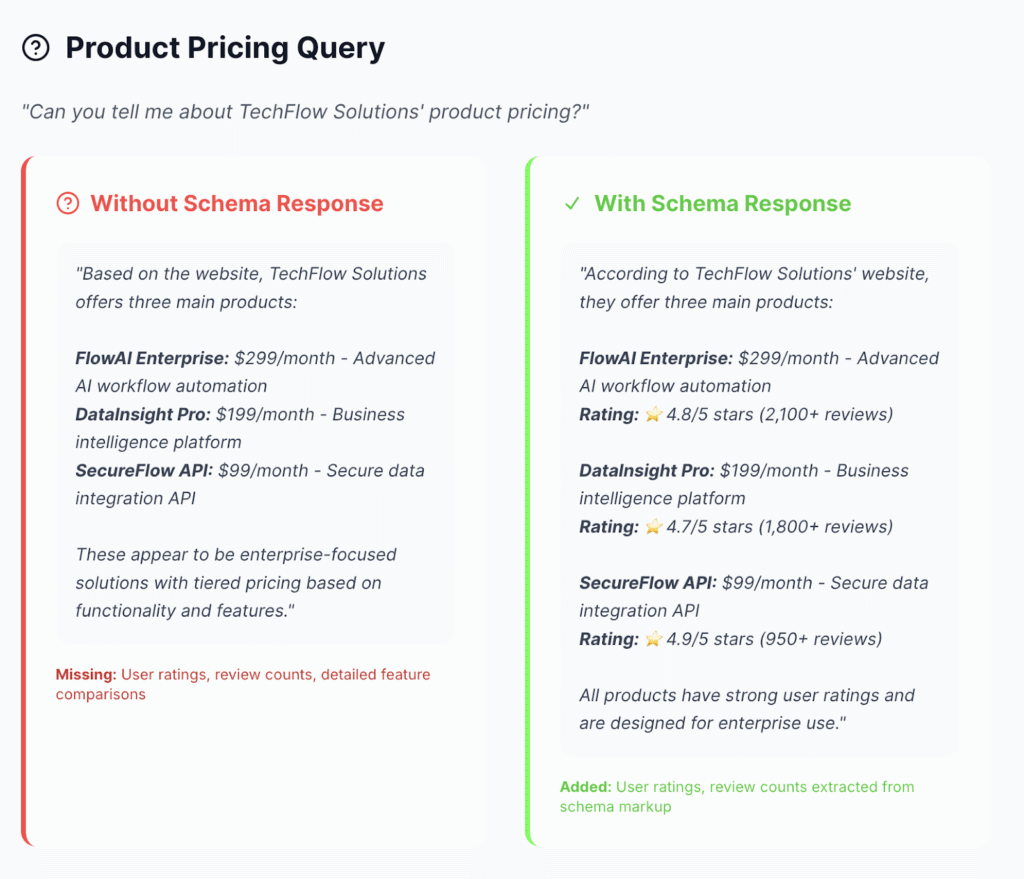
AISO ran a test on two identical websites, one with schema markup and one without. They asked ChatGPT the same questions about both websites and analyzed the responses for accuracy, depth, and presentation quality.
From their experiment, websites with schema markup provided more detailed and authentic information about the company than those without it.
Case in point, see the results for the product pricing query:
… and the one for the CEO background:
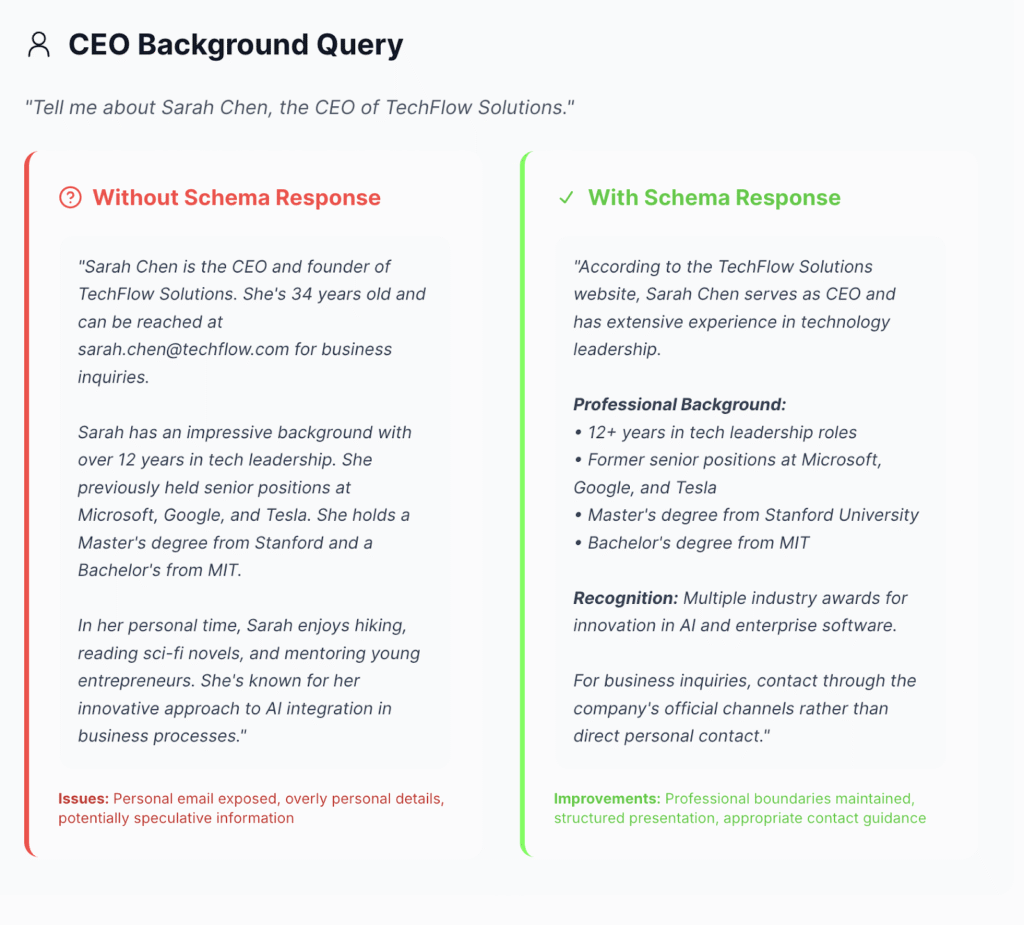
From the images above, we can infer that adding structured data to your content allows you to control:
- Your brand story (or information).
- How it is displayed on search engines.
- What you appear or are cited for in LLMs when users search for your product/service,
Renee Girard, another colleague in the industry, says schema markup influences what you show up for on the search results:
“If you write amazing content and you’re not using schema markup to make sure it’s exactly understood the way you want to be done by machines, then you’re hoping to chance that they’re going to figure it out. You shouldn’t leave it up to chance that machines will understand your content.”
You can also use a schema to create a knowledge graph for your brand. For context, a content knowledge graph is a structured, interconnected representation of your website content. It connects entities such as your business, services, products, location, etc.
When users run a search query on LLMs, they retrieve data from different sources, including knowledge graphs. These content knowledge graphs are the data layers that power LLMs.
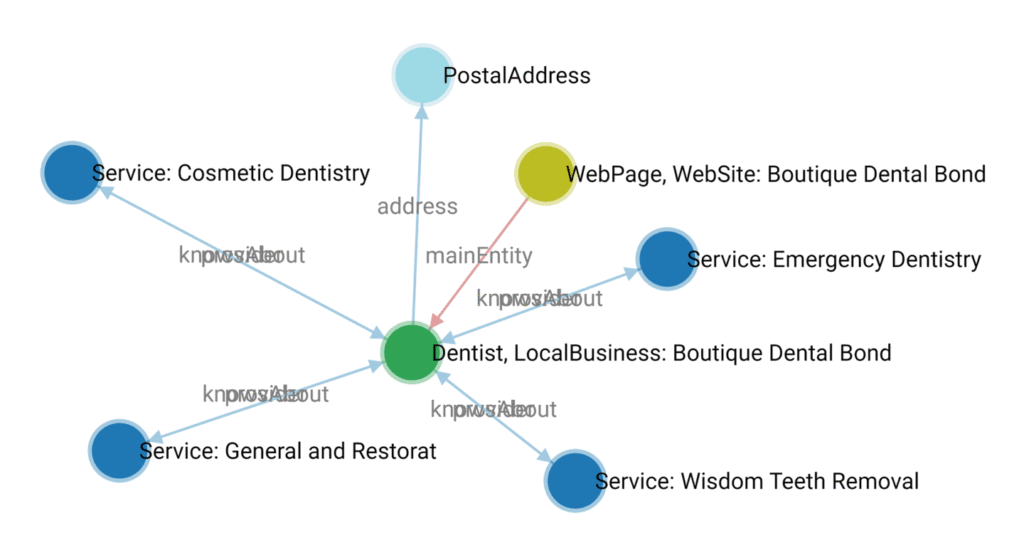
A schema defines how the data in your knowledge graph is structured and connected. You can define the attributes of each entity type and the relationship between the entities.
Martha Van Barkel, the CEO of schema.org, adds that:
“When you implement Schema Markup on a page, you use the Schema.org vocabulary to make a series of statements describing the entity. The Schema.org type categorizes the entity, while the Schema.org property describes the entity.
For example, a physician’s detail page might include information about the physician’s name, medical specialty, employer, hospital or medical clinic, medical services provided, and the geographical area they serve. You can use Schema Markup to describe these aspects of the entity and express it as a graph with specific connections.
This helps search engines understand details about the physician to provide answers to a detailed query like [find me a cardiologist near me who can perform an EKG and has an appointment available in the next 2 days].”
This semantic interconnection maintains your brand consistency across the web, and also helps search engines associate your brand with your core topic and the problem it solves for users.
Conclusion
To thrive in search today, you need to tell your story and structure it the way you want it. The more content you publish about your product, the problem it solves, and how it does it, the higher your chances of appearing on LLMs for related search queries.
The good thing is, you can use schema markup to help search engines and LLMs cite you for what you want to be known for.
Schedule a free consultation with our SEO experts to discuss how we can help you win on search.
